In recent years, the demand for advanced thermal management has continued to rise across electronics, 5G communications, new energy vehicles, and aerospace sectors — particularly with the rapid increase in AI GPU power consumption. Traditional heat sink manufacturing processes are beginning to reveal their limitations. Challenges such as the difficulty of processing complex microstructures, strict assembly precision requirements, and constraints on material selection have hindered further performance improvements.
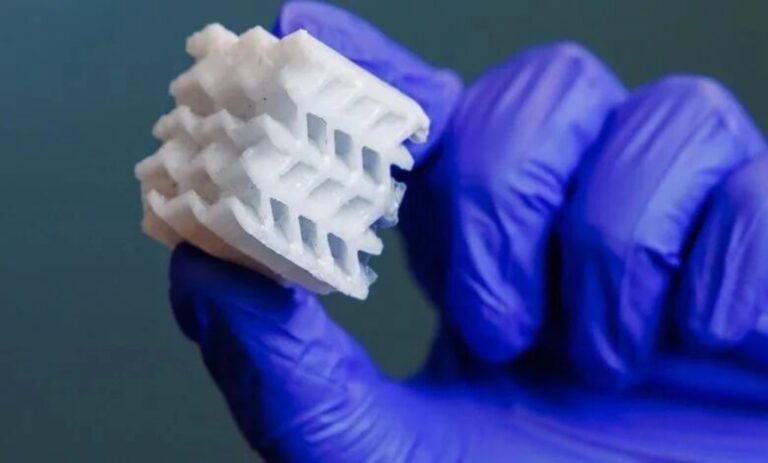
By leveraging metal 3D printing technology, Beifeng Intelligent has achieved a revolutionary breakthrough in heat sink research and application, enabling the production of ultra-thin 0.3 mm fin structures and opening the door to more efficient, lightweight, and design-flexible thermal management solutions.

From Traditional Processes to 3D Printing: The Inevitable Choice for Technological Innovation
In the traditional manufacturing process of thermal components such as VC (Vapor Chamber) heat sinks and microchannel cold plates, production steps are complex and involve multiple challenges, including:
Difficulty in Capillary Structure Fabrication:
Maintaining uniform pore size and thickness in the sintered layer is challenging, which can easily lead to clogging or poor fluid return.
Issues with Vacuum Brazing:
Uneven bonding surfaces and internal contaminants can result in weak joints or deformation.
Limitations of Microchannel Machining:
Traditional 2D manufacturing techniques cannot meet the demand for complex 3D structures, while welding deformation and sealing risks remain difficult to overcome.
VC Heat Sinks and Microchannel Cold Plates
These bottlenecks have long restricted the design freedom and performance potential of heat sinks. The introduction of 3D printing has completely broken these limitations.
Beifeng Intelligent leverages Selective Laser Melting (SLM) technology to form complex capillary channels, heterogeneous porous structures, and integrated flow channel housings in a single build. This not only significantly reduces the number of manufacturing steps but also eliminates the risk of leakage caused by traditional welding.
Four Key Advantages of 3D-Printed Heat Sinks
The technological breakthroughs of 3D printing in the field of heat sinks are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
Design Freedom & Monolithic Integration
3D printing can directly produce complex capillary structures such as honeycomb, zoned porosity, and dendritic shapes, while integrating them with the upper and lower shells, support pillars, and flow channels in one piece.
This integrated design eliminates alignment errors and weak joints common in traditional processes, resulting in more reliable thermal modules — especially suitable for customized cooling solutions in high-density electronics such as laptops and 5G modules.
Material Breakthroughs & Extreme Environment Adaptability
Traditional VC heat sinks are almost exclusively made of copper. Beifeng Intelligent has expanded its 3D printing process to include titanium alloys, aluminum alloys, stainless steels, and high-temperature Inconel alloys.
For example, its self-developed GA520 high-strength aluminum alloy offers excellent yield strength and elongation performance and supports anodizing treatment. This means 3D-printed heat sinks can operate reliably in high-temperature, corrosive, and high-vibration environments, greatly expanding their application prospects in aerospace and defense sectors.
| Sample Material | Test Temperature (°C) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
| GA520 | 23 | 490 – 590 | 470 – 570 | 10 – 15 |
Process Optimization for High-Performance Assurance
Through density-optimization techniques, the porosity of printed parts is reduced to below 0.3%, achieving a density of nearly 99.7%, far exceeding conventional requirements. In terms of surface roughness, process optimization combined with post-processing brings the outer surface down to 0.6 μm and the internal flow channels as low as 2.2 μm, effectively achieving a mirror-like finish.
These breakthroughs ensure smooth fluid circulation and significantly enhance heat dissipation efficiency.
At the same time, by controlling residual stress and optimizing auxiliary supports, Beifeng Intelligent effectively resolves warping issues in thin-walled structures. As a result, heat sink wall thickness can be reduced to 0.3 mm, and internal channel widths are controlled to 0.143 mm, far surpassing the precision achievable with traditional manufacturing methods.
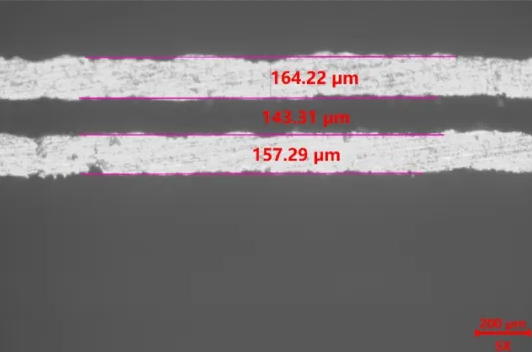
3D-Printed Heat Sink Wall Thickness and Flow Channel Testing
Rapid Iteration and Scalable Production
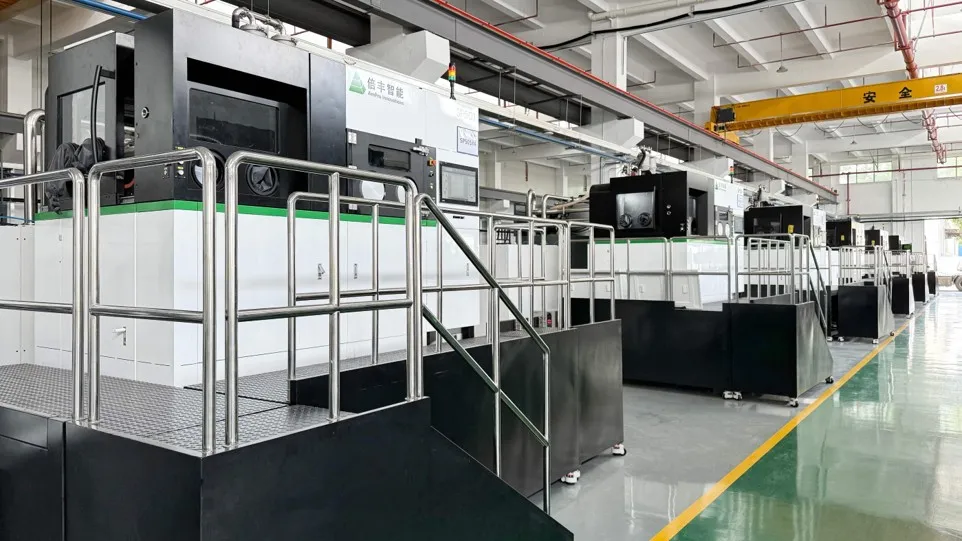
The “CAD-to-physical-part” workflow of 3D printing dramatically shortens the R&D and validation cycle, making it possible to customize VC structures for specific high-heat-flux chips. Beifeng Intelligent has built a large-scale production workshop with over 100 additive manufacturing machines, enabling full coverage from R&D to mass production. This not only meets small-batch customization needs but also drives the transition of intelligent heat sinks toward large-scale manufacturing.
Full-Process Validation: From Airtightness to Flow Performance
As a critical component of thermal management systems, the reliability of heat sinks must be rigorously validated. Beifeng Intelligent has established a comprehensive testing framework throughout product development:
Airtightness Testing: Products pass both positive-pressure (0.2 MPa, 60-second hold) and negative-pressure tests with zero leakage; helium leak detection confirms full compliance.
Evaporation & Permeation Testing: Long-duration tests at 65 °C show no bulging or weight loss, indicating excellent long-term stability.
Flow Performance Testing: Capillary water injection tests confirm smooth liquid circulation with no leakage.
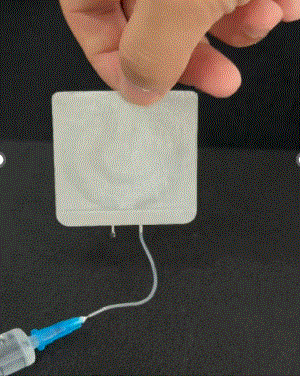
Sample Water Injection Test: During the process, no leakage was observed, and the outflow rate remained smooth and stable.
These experimental results fully demonstrate that 3D-printed heat sinks are fully capable of replacing – and even surpassing – traditional products in terms of reliability and stability.