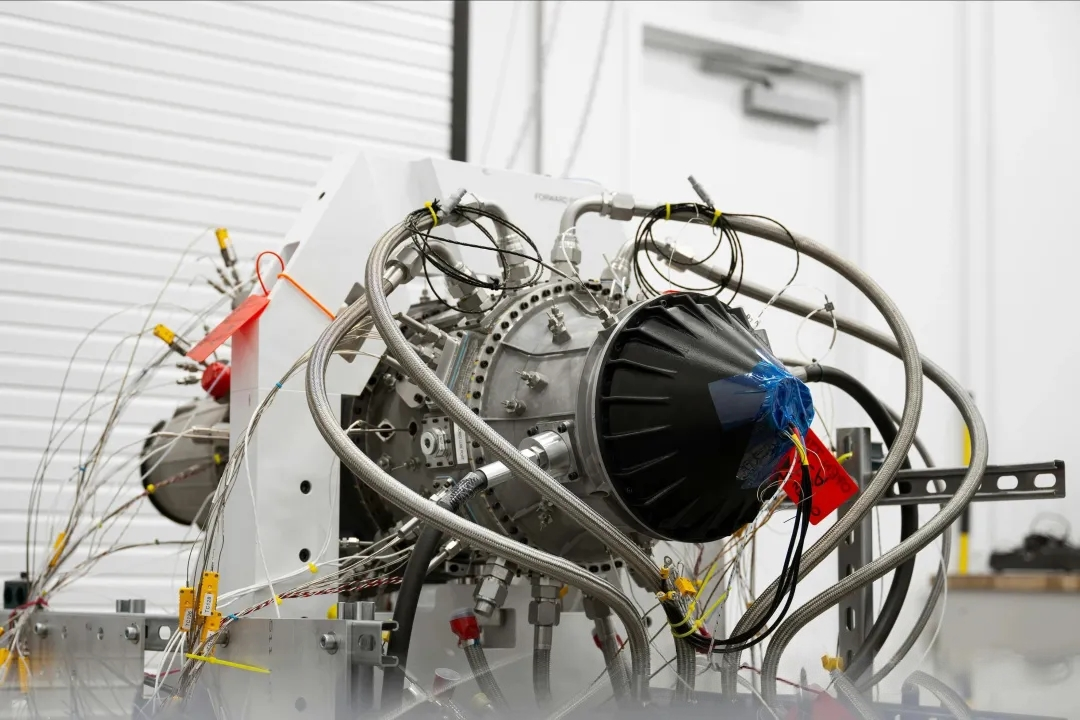
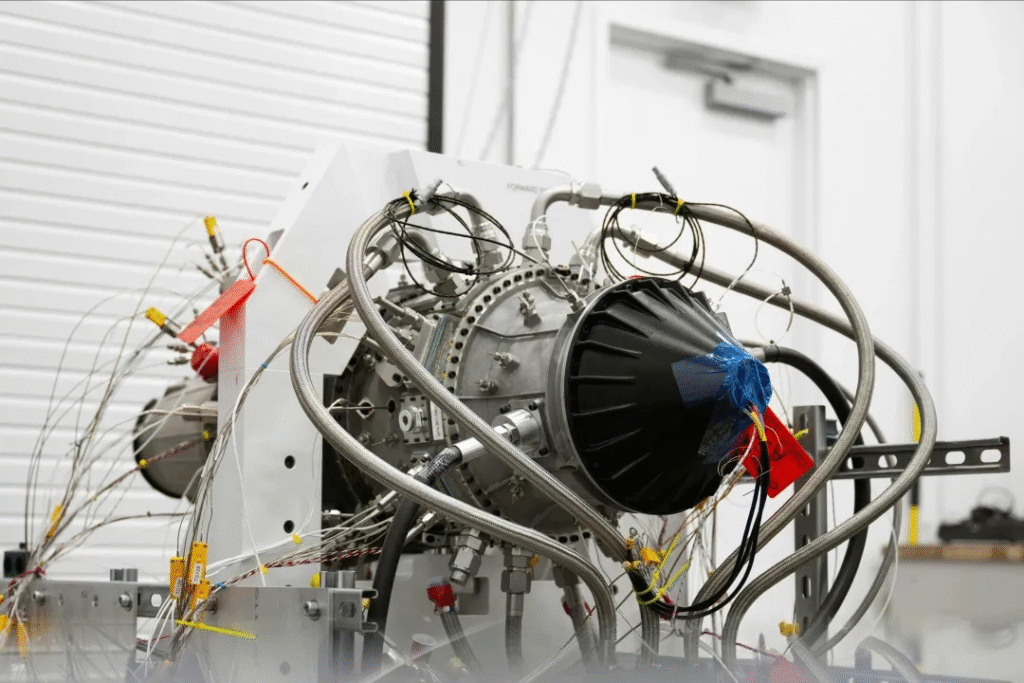
U.S.-based company Beehive Industries recently announced that its 200-pound-thrust, 3D-printed Frenzy engine, developed for the U.S. Air Force, has successfully completed high-altitude testing.
The successful test has attracted strong interest from U.S. defense contractors and potential customers, particularly those focused on the development of autonomous combat aircraft, which feature a high degree of intelligence and automation.
Why it matters?
High-altitude testing is a critical step in validating an engine’s performance in real flight conditions—especially in environments characterized by thin air, low pressure, and low temperatures. It is particularly important for assessing the reliability of 3D-printed engines under extreme conditions.
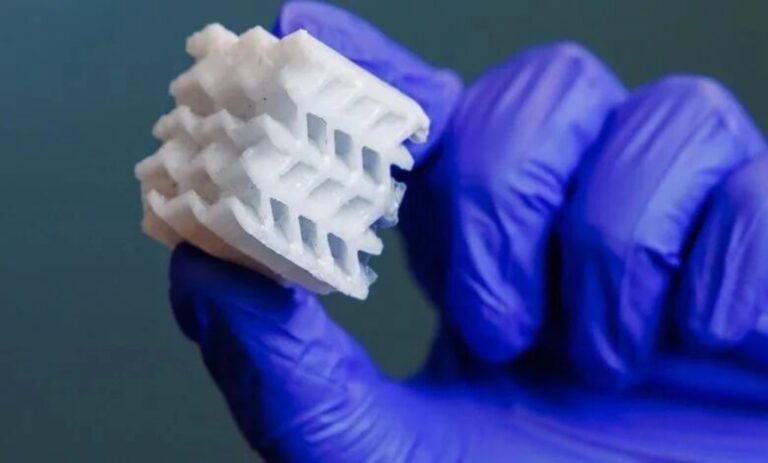
While the phrase “the engine is 3D-printed” may sound simple, it usually implies profound changes to the internal structure. These often include thin-walled features, lattice structures, integrated flow channels, and topology-optimized geometries. Whether such structures can withstand extreme environments without deformation, cracking, or other failure modes directly determines whether the engine can be practically and reliably deployed.

Therefore, Beehive Industries described this test as a milestone achievement, meaning the engine can now move out of the laboratory and proceed to real flight testing.
Meanwhile, a 3D-printed minimalist turbojet engine independently developed by AECC (Aero Engine Corporation of China) completed its first flight test last month, reaching an altitude of 6,000 meters—undeniably a high-altitude flight as well. While the phrase “marking an important breakthrough in the engineering application of 3D-printed engines” may sound simple, reflecting on it more deeply reveals just how significant this achievement truly is.

Ultra-Fast Development, Iteration, and Testing Enabled by 3D Printing
Beehive Industries explained that Frenzy is a new type of small jet engine developed almost entirely through digital design and 3D printing technologies. This approach enables rapid prototyping, fast iterative improvements, and simplified production processes. The engine’s development timeline was remarkably short: within four months, the company completed ground testing of six engines, after which two prototypes were transported to Ohio for high-altitude testing. During these tests, engineers evaluated ignition performance, low-pressure stability, fuel consumption, and thermal behavior under extreme conditions.
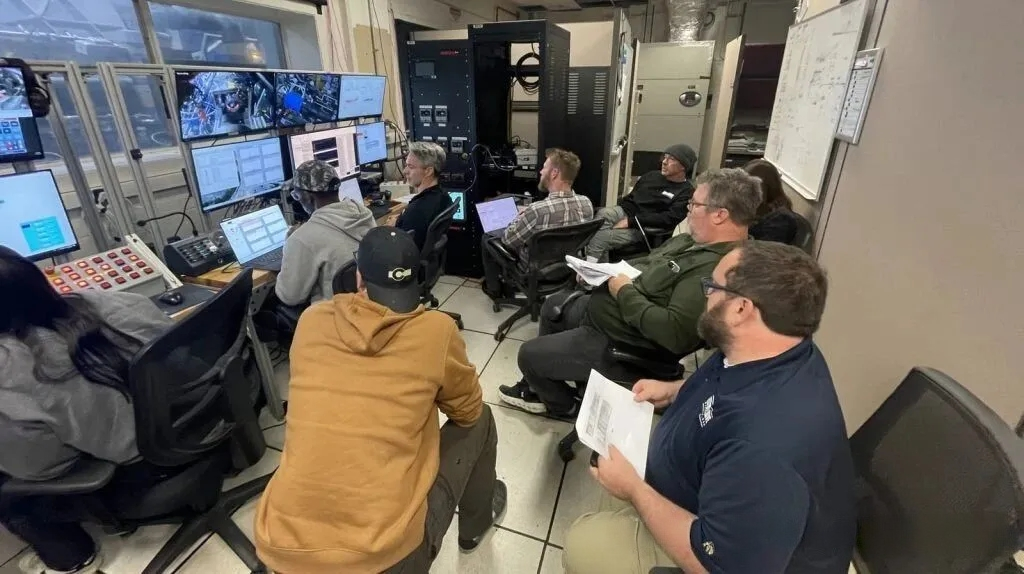

The engine demonstrated reliable ignition and stable operation across the full flight envelope, with rapid acceleration from ignition to full power. Turbine temperature and fuel consumption data exceeded initial expectations, and even after operating for a duration equivalent to a full mission life, the engine remained in “like-new” condition.
Given the unique loading conditions that small turbine engines experience in high-altitude environments, these results are particularly significant. Stable ignition and smooth acceleration are critical for high-volume, cost-sensitive propulsion systems used on unmanned platforms. This successful test is expected to enable Beehive Industries to begin flight testing of the engine in early 2026, aligning well with the U.S. Department of Defense’s efforts to identify scalable propulsion solutions for unmanned aerial systems.
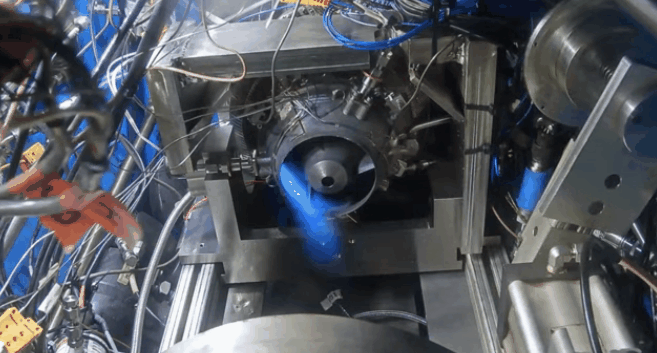
Future Challenges and Industry Impact
3D printing technology is driving advancements in the defense sector by dramatically shortening the time from engine design to testing. This rapid iteration capability is highly valued by militaries around the world.
Beehive Industries has adopted an “additive-first” strategy, emphasizing fast cycles of printing, testing, optimization, and reprinting engine components. As the defense sector shifts toward high-volume, rapidly evolving unmanned systems, Beehive’s progress is likely to intensify competition across the industry. Major players such as Pratt & Whitney, GE Aerospace, Rolls-Royce, and Honeywell Aerospace are expected to accelerate their own engine development efforts and target emerging markets for autonomous unmanned platforms.