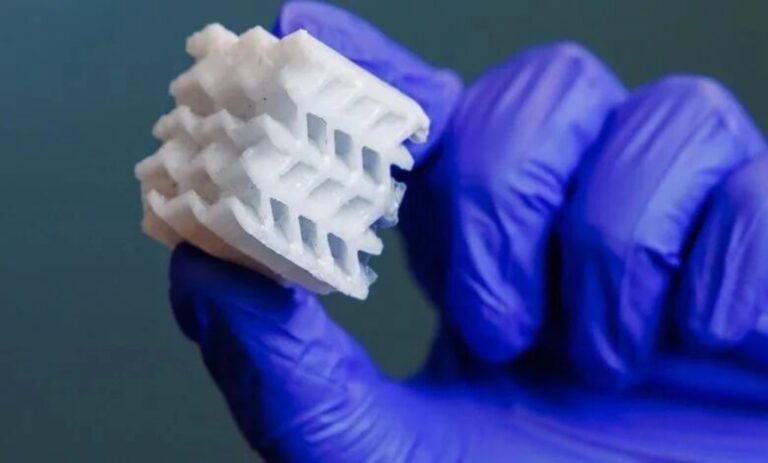
For a long time, support structures in additive manufacturing (AM) have been a necessary trade-off—they provide stability, but at the cost of consuming more material, extending build times, and requiring extensive post-processing.
However, advances in low-angle printing technology are redefining these limitations, allowing manufacturers to move beyond traditional heavy-support designs. For the AM industry, this shift unlocks new possibilities for both internal designs and external geometries—capabilities that were previously impossible to achieve. This not only improves part strength and efficiency but also enhances sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and reduces post-processing requirements.
By eliminating such constraints, low-angle printing is transforming the design, fabrication, and production scale of AM components.
Expanding Application Fields
Traditionally, low-angle printing has been closely associated with high-value applications in aerospace and energy sectors, such as impellers, turbine components, or stator rings. Yet its benefits extend far beyond these areas.
From space to automotive, consumer goods to medical devices, manufacturers are increasingly leveraging low-angle printing to achieve the following goals:
Greater design freedom:
Reduced need for internal supports enables new possibilities for complex geometries and application-specific designs.
Lower material usage and production cost:
Fewer supports mean less material consumption and significant cost savings.
Faster production and simplified post-processing:
Less support reduces printing time and minimizes post-print removal work.
Improved cooling efficiency:
Larger, unconventional cooling channels can be printed, enhancing mold performance.
Higher accuracy in fine features:
Exceptional dimensional precision makes it ideal for thin walls and intricate structures.
Enhanced surface quality:
Better aesthetics and functionality, especially on downward-facing surfaces.
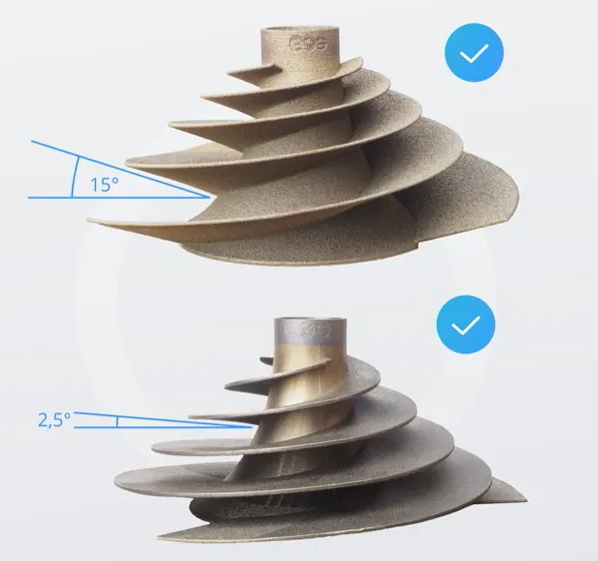

Demonstration Parts Printed at Low Angles (15° and 2.5°)
Sustainability and Lifecycle Impact
A growing number of consumers are prioritizing sustainability: 85% report that climate change has already disrupted their daily lives, and 63% confirm the importance of environmentally friendly products. As a result, sustainability is rapidly becoming the foundation of all forward-looking business strategies.
Compared with subtractive manufacturing, additive manufacturing (AM) has always offered material efficiency advantages. Now, advanced low-angle printing strategies further amplify these benefits, helping manufacturers achieve their sustainability goals.
By minimizing or even eliminating support structures, manufacturers can reduce material waste, energy consumption, and post-processing efforts. Lifecycle assessments of low-angle printing versus conventional AM methods reveal significant benefits:
Lower powder consumption:
Fewer supports mean less wasted material.
Reduced print time and post-processing:
Faster builds and less support removal lead to energy savings.
Extended part lifespan:
Optimized geometries enable better heat dissipation and reduce stress concentrations, enhancing durability.

Improved Surface Quality
By intelligently applying heat to the lower surface regions, we have enhanced the print quality of low-angle geometries without adding extra wait time. This method, originally derived from SmartFusion, has now been adapted into specific print configurations that stabilize overhanging surfaces and reduce defects. When combined with optimized exposure strategies, it ensures that low-angle features remain strong and manufacturable.
For OEMs seeking to strengthen their sustainability capabilities, adopting low-angle printing is also a way to demonstrate a clear commitment to responsible manufacturing
User Experience and Software Evolution
One of the greatest barriers to AM adoption has historically been the complexity of design software. However, continuous advancements in printing technology are making low-angle printing easier than ever before.
Modern software solutions now offer:
Automated optimization – enabling users to experiment with low-angle designs without requiring deep technical expertise.
Real-time simulation and analysis – ensuring part manufacturability and performance before printing begins.
Enhanced intuitive interfaces – empowering designers and engineers to iterate products quickly and confidently.
For industries with extremely high demands for precision and repeatability, these advancements mean manufacturers can push design boundaries without facing a steep learning curve.
Scaling Up: From Prototyping to Mass Production
While low-angle printing demonstrates clear advantages in prototyping, its true test lies in scalability for production. Fortunately, as the technology matures, large-scale manufacturing is becoming increasingly feasible.
Key factors influencing scalability include:
Process repeatability – ensuring consistent quality across batch production.
Improved post-processing efficiency – minimizing support removal needs to shorten turnaround times.
Integration with hybrid manufacturing – combining printed mold inserts with traditional machining for optimal performance.